Data Protection: Safeguarding Information in a Digital World
In today’s data-driven economy, protecting sensitive information is critical. Whether you're a consumer safeguarding personal details or a business managing client records, data protection is essential for trust, compliance, and operational integrity.
What Is Data Protection?
Data protection refers to the strategies, policies, and technologies used to secure data from unauthorized access, corruption, theft, or loss. It ensures that information remains confidential, available, and accurate.
Why Data Protection Matters
🔒 Security & Privacy: Data breaches can expose personal or corporate information, leading to identity theft or competitive disadvantage.
📜 Regulatory Compliance: Laws like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA mandate strict data management practices with heavy penalties for violations.
💼 Reputation Management: A data leak can permanently damage a company’s credibility with customers, partners, and investors.
💻 Business Continuity: Reliable data backups and protection systems ensure operations can resume after cyberattacks or natural disasters.
Key Principles of Data Protection
- Data Minimization: Collect only the data you truly need.
- Access Control: Limit data access to authorized personnel only.
- Encryption: Protect data in transit and at rest with advanced encryption methods.
- Regular Backups: Maintain secure, off-site backups to ensure data recovery.
- Transparency: Inform users about what data is collected and how it’s used.
Common Data Protection Measures
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Firewalls & Antivirus | Basic defense against malware and unauthorized access |
| Encryption Protocols | Secures sensitive data with encoding technology |
| Multi-Factor Authentication | Adds extra layers of user verification |
| Cloud Backups | Protects data from local hardware failures |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | Tools to prevent data leaks through email, USB, etc. |
Business-Specific Strategies
- Employee Training: Ensure staff know how to handle and secure sensitive data.
- Audit Trails: Keep logs of who accessed what data and when.
- Vendor Risk Management: Assess third-party service providers for compliance and security.
- Incident Response Plan: Be ready to detect, report, and resolve data breaches quickly.
Data Protection Regulations
- GDPR (EU): Applies to any company handling EU citizen data. Emphasizes consent and the right to be forgotten.
- CCPA (California): Requires transparency in data collection and allows users to opt out.
- HIPAA (U.S. healthcare): Protects patient health information.
- FERPA (U.S. education): Governs access to student education records.
Future Trends in Data Protection
- AI & Machine Learning: Used for threat detection and automated security responses.
- Zero Trust Architecture: Assumes no user or device is trusted by default.
- Data Sovereignty: Growing importance of storing data within national borders.
Conclusion
Effective data protection isn’t optional—it’s a necessity. With rising cyber threats and strict regulations, businesses and individuals must prioritize how information is collected, stored, and shared. By adopting best practices and staying informed, you can reduce risks and build digital trust.
Explore

Secure Data Protection Services: Safeguarding Your Business and Personal Data
Top Cloud Security Providers: Safeguarding Your Data in the Digital Age

Guarding Your Digital Fortress: Essential Data Protection Services for a Safer Tomorrow

Data Security Management: Essential Strategies for Protection

What Is Data Protection and Why It Matters in 2025

Affordable Cloud Security: Protect Your Data Without Breaking the Bank

Best Cloud Security Services to Protect Your Business Data
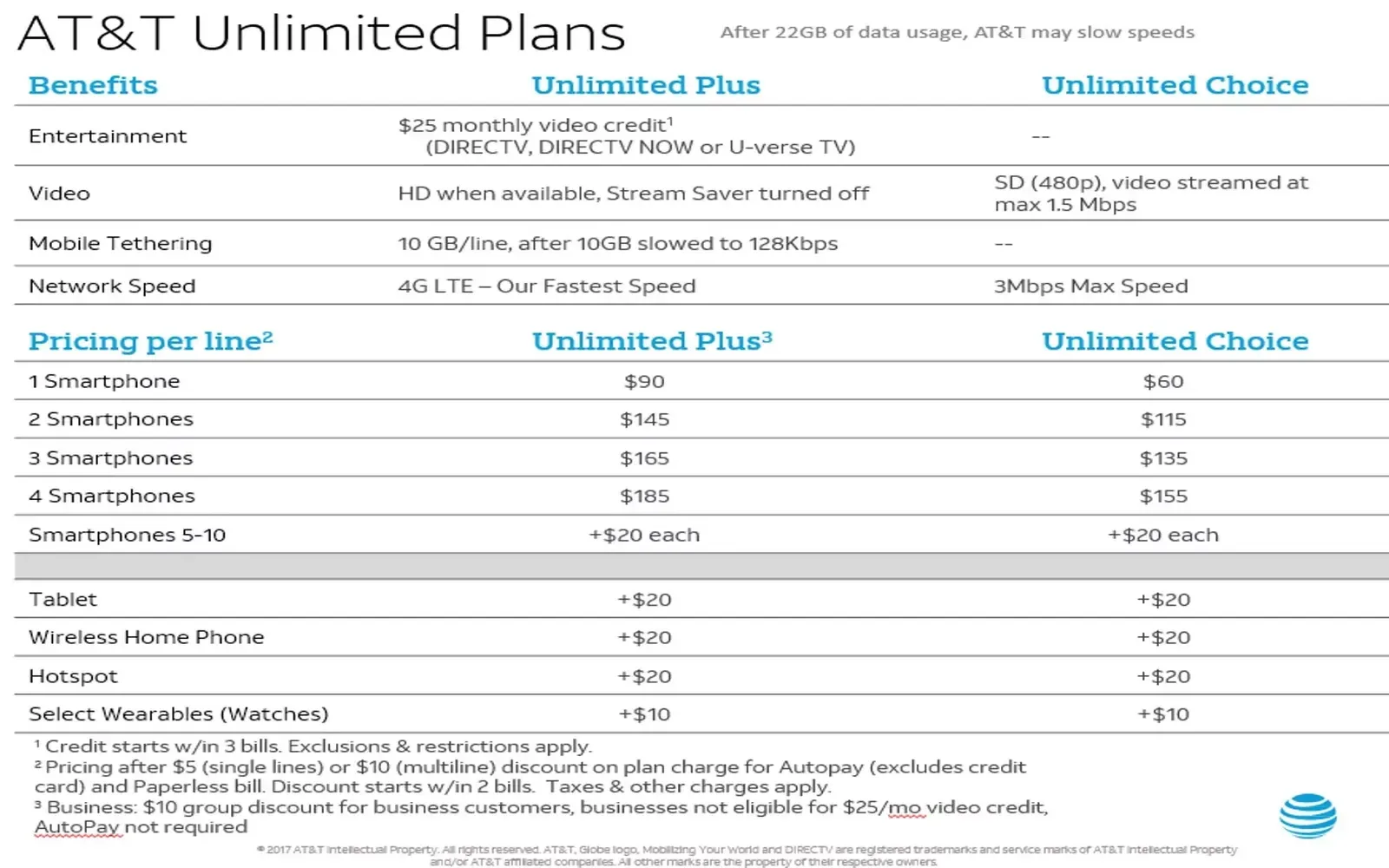
Top 10 Best Unlimited Data Plans: Uninterrupted Browsing and Streaming!
